How to Safely Remove IVC Filters and What You Need to Know
In the field of vascular medicine, the safe removal of inferior vena cava (IVC) filters has garnered significant attention due to its implications for patient outcomes and overall safety. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in the IVC removal industry, emphasizes the importance of a meticulous approach: "The key to successful IVC filter removal lies in understanding the individual patient's needs and the potential risks involved." This statement underscores the critical nature of personalized medical strategies in enhancing the efficacy of IVC filter retrieval procedures.
As the utilization of IVC filters rises, alongside concerns about their long-term presence in the body, the discussion around IVC removal techniques becomes increasingly pertinent. Knowing how to safely remove these devices not only mitigates the risk of complications but also improves the quality of life for patients who may be burdened by these devices after the resolution of their initial medical condition.
This article aims to provide essential insights regarding the IVC filter removal process, outlining the key considerations and best practices that both healthcare providers and patients should be aware of. By highlighting expert opinions and current methodologies in IVC removal, we hope to enhance understanding and facilitate informed decision-making among those navigating this intricate landscape.
Understanding IVC Filters: Purpose and Types
IVC filters, or inferior vena cava filters, are medical devices designed to prevent life-threatening pulmonary embolisms by trapping blood clots that may travel from the lower body to the lungs. These filters are typically recommended for patients who are at high risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) but cannot take anticoagulant medication due to various reasons, such as allergies or active bleeding. Understanding the purpose of IVC filters is crucial, as they play a key role in managing patients' vascular health and preventing serious complications.
There are different types of IVC filters, including permanent and retrievable models. Permanent filters are designed for long-term use and are typically implanted for patients with chronic conditions that necessitate ongoing protection against blood clots. On the other hand, retrievable filters can be removed once the patient’s risk of DVT has diminished, offering an option that reduces the risks associated with long-term implantation, such as filter migration, perforation, or thrombosis.
Selecting an appropriate type of IVC filter involves careful consideration of the patient's medical history, risk factors, and overall health status, highlighting the importance of individualized patient care when utilizing these devices.
Indications for Removal of IVC Filters
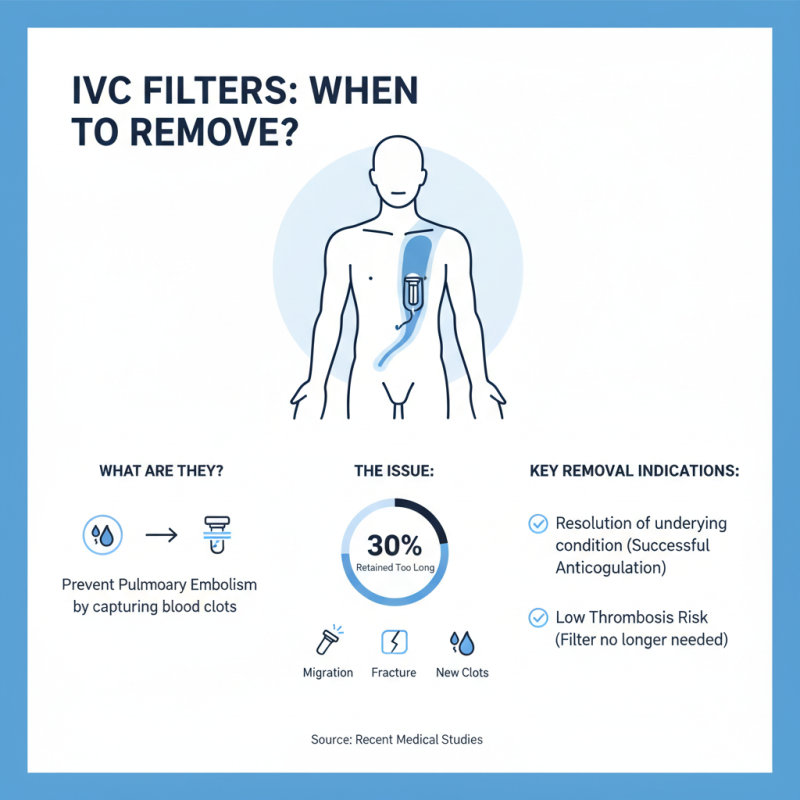
IVC filters, or inferior vena cava filters, are devices implanted to prevent pulmonary embolism by capturing blood clots in the inferior vena cava. However, the need for their removal arises under specific clinical indications. According to recent studies, approximately 30% of IVC filters are retained beyond the necessary period, which can lead to complications such as filter migration, fracture, or development of new clots. The key indications for IVC filter removal include resolution of the patient’s underlying condition, typically after a successful anticoagulation therapy, or instances where the filter is no longer deemed necessary due to a low risk of thrombosis.
To ensure patient safety during the removal process, healthcare professionals must evaluate the filter’s position and assess for any complications that may hinder removal. The American College of Chest Physicians recommends that IVC filters should ideally be retrieved within a few weeks to months post-placement, especially if no clear benefit is observed in prolonged filtering. This reduces the risk of long-term complications significantly, based on observational studies indicating that filter-related complications decrease by over 50% when filters are removed in a timely manner.
Tips for Successfully Planning IVC Filter Removal:
1. Schedule regular imaging studies post-placement to monitor the filter's status and complications that may arise.
2. Maintain open communication with the healthcare team, ensuring that changes in the patient’s condition are promptly addressed to facilitate timely removal planning.
3. Educate patients regarding the importance of follow-up appointments and the necessity of filter retrieval to avoid potential health risks associated with retained filters.
Preparation and Pre-Removal Considerations
Before proceeding with the removal of an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter, thorough preparation is essential to ensure a safe and effective procedure. Patients should have an open discussion with their healthcare providers to understand the risks and benefits associated with filter removal. A comprehensive medical history should be reviewed, alongside any recent imaging studies, to assess the filter's position and the surrounding anatomy. This information helps to identify any potential complications that could arise during the removal process.
In addition to evaluating the physical health and imaging results, preparing mentally and emotionally is also vital for the patient. Understanding the procedure, what to expect during recovery, and how to manage any post-removal symptoms can significantly alleviate anxiety. Patients are often advised to arrange for post-procedure transportation, as they may experience grogginess or discomfort from sedation if it is used during the process. Taking these preparatory steps can facilitate a smoother experience and contribute to better overall outcomes.
Steps for the Safe Removal of IVC Filters
When it comes to the safe removal of inferior vena cava (IVC) filters, healthcare professionals must adhere to specific steps to minimize risks and enhance patient outcomes. IVC filters are designed to prevent life-threatening pulmonary embolisms by capturing blood clots, but their long-term presence can lead to complications such as filter migration, fracture, or thrombosis. According to a study published in the *Journal of Vascular Surgery*, the risk of complications increases significantly after five years of filter placement, underscoring the importance of timely removal when it is no longer needed.
The first step in the safe removal process involves proper patient assessment and imaging studies to evaluate the filter's position and any associated complications. A detailed plan, including pre-procedural anticoagulation management, is essential to reduce the risk of thromboembolic events during the removal procedure. Aftercare is equally vital; a report from the *American Journal of Cardiology* indicates that patients monitored closely post-removal experience a substantially lower incidence of adverse events, reinforcing the need for thorough post-operative evaluation. In conclusion, adherence to these critical steps can significantly impact the safety and effectiveness of IVC filter removals, contributing to improved patient care and outcomes.
How to Safely Remove IVC Filters and What You Need to Know - Steps for the Safe Removal of IVC Filters
| Step | Description | Precautions | Recovery Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate the need for removal. | Ensure proper medical clearance. | Follow post-op care instructions provided by your doctor. |
| 2 | Schedule a procedure for filter removal. | Ensure you understand the process and its risks. | Maintain hydration and healthy nutrition for recovery. |
| 3 | Undergo a minimally invasive extraction method. | Discuss anesthesia options and consult anesthesiologist. | Rest and monitor for any unusual symptoms post-procedure. |
| 4 | Follow up with your doctor for imaging studies to confirm removal. | Stay aware of any signs of complications. | Engage in light activity as advised by your healthcare team. |
| 5 | Maintain regular check-ups to monitor overall health. | Report any unexpected changes in health immediately. | Stay informed about your health status and follow medical advice. |
Post-Removal Care and Monitoring for Patients
Post-removal care and monitoring are crucial for patients who have undergone IVC filter removal. After the procedure, patients should closely observe for any signs of complications such as swelling, redness, or pain at the insertion site. It is essential to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding post-operative care, which may include activity restrictions and wound care. Patients are often advised to avoid strenuous activities for a period to allow proper healing, minimizing the risk of bleeding or infection.
Additionally, monitoring for any changes in health status is vital. Patients should be aware of symptoms such as sudden leg swelling, persistent headache, or shortness of breath, as these could indicate potential complications. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are necessary to assess recovery and to conduct any imaging studies if required. It’s also important that patients maintain a healthy lifestyle post-removal, including staying hydrated and adhering to any prescribed medication regimens, to reduce the risk of further venous issues. Engaging in discussions with healthcare professionals about any concerns can facilitate better recovery outcomes and ensure patient safety.
IVC Filter Removal Outcomes and Post-Removal Monitoring
Related Posts
-
10 Essential Tips for Effective IVC Removal You Need to Know
-

2025 Top Hemostatic Pads for Effective Wound Management and Rapid Healing
-

Achieve Needle: 2025's Top 10 Innovative Tools for Success
-
Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Catheter Drainage Bag for Optimal Comfort and Care
-
Understanding the Importance of Luer Stopcocks in Fluid Management Systems for Healthcare Efficiency
-

Top Arrow Arterial Line Kit Benefits and Usage in Intensive Care Units